Paediatrics MCQs for AMC Part 1 Exam
Question 4011
A 6-month-old infant is brought to the emergency department with vomiting, and “redcurrant jelly” stools. On examination, you palpate a sausage-shaped mass in the right upper quadrant of the abdomen. The infant appears lethargic and has episodes of inconsolable crying. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Appendicitis
- B) Intussusception
- C) Meckel’s Diverticulum
- D) Hirschsprung’s Disease
- E) Pyloric Stenosis
Question 4012
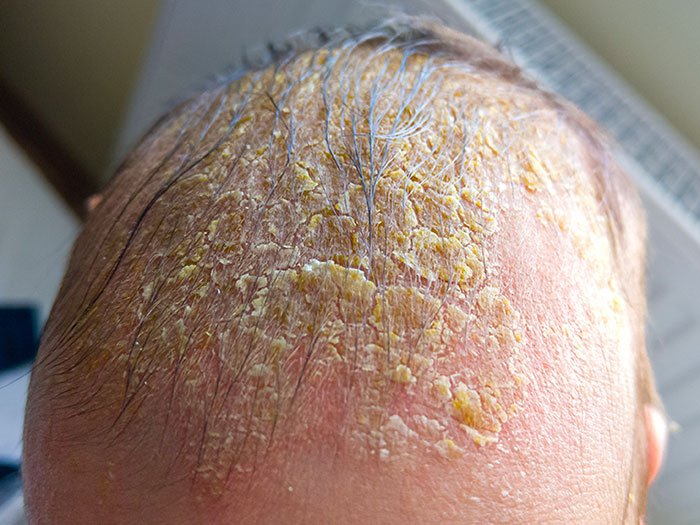
A 3-month-old infant is brought to the paediatrician with a scalp rash. The infant is otherwise healthy and thriving. Physical examination reveals no abnormal findings. Which of the following is the most appropriate next step in managing this infant’s condition?
- A) Prescribe a topical antifungal cream
- B) Perform a skin biopsy for further evaluation
- C) Initiate oral antibiotic therapy
- D) Administer oral corticosteroids
- E) Advise to apply moisturizer and use a comb to remove scales when bathing
Question 4013
A 8-year-old girl is brought to the paediatric clinic by her mother who reports that the child has been complaining of perianal itching for the past several weeks. The mother notes that the itching is more noticeable at night. On examination, there is no redness or rash in the perianal area, but small, white, thread-like structures are observed on the perianal skin and in the child’s underwear. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Giardiasis
- B) Candidiasis
- C) Enterobius Vermicularis Infestation
- D) Roundworm Infestation
- E) Scabies
Question 4014
A 3-year-old child is brought to the pediatrician with a high-grade fever persisting for five days. On examination, you note bilateral non-exudative conjunctivitis, erythema of the lips, and a “strawberry tongue.” The child also has swollen hands and feet with desquamation of the fingertips. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Scarlet Fever
- B) Measles
- C) Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
- D) Kawasaki Disease
- E) Toxic Shock Syndrome
Question 4015
A 4-year-old child is diagnosed with Kawasaki Disease based on clinical criteria. What is the primary treatment to reduce acute symptoms and the risk of coronary artery complications in this patient?
- A) 3rd generation cephalosporins
- B) Acyclovir
- C) Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
- D) IV Corticosteroids
- E) Aspirin
Question 4016
A 2-year-old child presents with a high fever for the past three days, which has abruptly resolved. Following the fever, a faint maculopapular rash has appeared on the trunk and spreading to the extremities. The child’s parents report irritability during the febrile phase. On examination, there are no signs of conjunctivitis, changes in the lips, or oedema of hands and feet. What is the most likely diagnosis?
- A) Scarlet Fever
- B) Roseola Infantum
- C) Hand, Foot, and Mouth Disease
- D) Kawasaki Disease
- E) Henoch-Schönlein Purpura
Question 4017
A 14-month-old infant is diagnosed with Roseola Infantum based on clinical features. The child has experienced high fever that has now resolved, and a maculopapular rash is present. What is the most appropriate management for this child?
- A) Acyclovir
- B) 3rd generation cephalosporins
- C) Topical Corticosteroids
- D) Supportive Care and Observation
- E) Intravenous Immunoglobulin (IVIG)
References
- https://www.rch.org.au/clinicalguide/guideline_index/intussusception/
- https://www.rch.org.au/kidsinfo/fact_sheets/Cradle_cap/
- https://www.nhs.uk/conditions/threadworms/
- https://www.racgp.org.au/getattachment/9125ecdc-7fd9-4339-8ebc-ce3ad73cfd72/Kawasaki-disease.aspx